Guide the students in class 12 A1, 12A2 at Quan Son high school to distinguish the language functions and responses exercises effectively
The globe today is the one of exchange, co-operation, integration and development. To reach the great progress like other countries, Vietnam has carried out many open-door policies and English has become an international language, an integral part, as a means to link countries together. It is utilized in almost aspects such as economy, politics, culture, science, diplomacy and so on. Therefore, English is becoming more essential to meet the demands of a free trade area (adopted in the ASEAN Vision 2020), studying English is definitely vital for students to pursue a good job in the future. English is becoming a compulsory subject in many exams, especially, the GCSE. English’s role and position in the modern society is highly respected. Thus, lots of students also choose English as a major subject to test in the entrance examination of the universities. So, English teachers who play very important roles always do want to find out the best way to convey the lessons effectively as well as motivate the students’ interest.
When guiding the students of class 12A1,12A2 at Quan Son high school to do some exercises related to language functions and responses I recognize that the students often feel confused and they usually make many mistakes. Their lack of practical tools to produce the actual language becomes evident. According to the form of tests for GCSE, there are two or three of fifty questions relating to language functions. Not many, but to give the correct answer in the important examination is the desire of all of the students. As an English teacher, I do the research for focusing on the functions of language so as to properly equip students to complete assigned tasks. Therefore; I choose the theme “Guide the students in class 12 A1, 12A2 at Quan Son high school to distinguish the language functions and responses exercises effectively” as my research. I hope that the information in this paper will be helpful in getting a deeper look about language functions and responses in English.
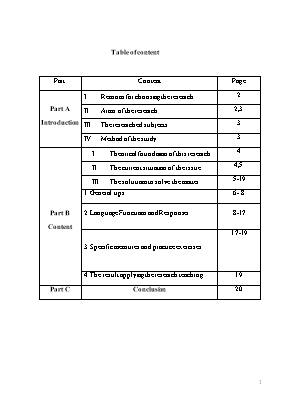
Table of content Part Content Page Part A Introduction Reasons for choosing the research. 2 Aims of the research. 2,3 The researched subjects. 3 Method of the study. 3 Part B Content Theorical foundation of this research 4 The current situation of the issue. 4,5 The solutions to solve the matter. 5-19 1. General tips 6- 8 2. Language Functions and Responses 8-17 3. Specific measures and practice exercises. 17-19 4. The result applying the research teaching. 19 Part C Conclusion 20 PART A: INTRODUCTION REASONS FOR CHOOSING THE RESEARCH The globe today is the one of exchange, co-operation, integration and development. To reach the great progress like other countries, Vietnam has carried out many open-door policies and English has become an international language, an integral part, as a means to link countries together. It is utilized in almost aspects such as economy, politics, culture, science, diplomacy and so on. Therefore, English is becoming more essential to meet the demands of a free trade area (adopted in the ASEAN Vision 2020), studying English is definitely vital for students to pursue a good job in the future. English is becoming a compulsory subject in many exams, especially, the GCSE. English’s role and position in the modern society is highly respected. Thus, lots of students also choose English as a major subject to test in the entrance examination of the universities. So, English teachers who play very important roles always do want to find out the best way to convey the lessons effectively as well as motivate the students’ interest. When guiding the students of class 12A1,12A2 at Quan Son high school to do some exercises related to language functions and responses I recognize that the students often feel confused and they usually make many mistakes. Their lack of practical tools to produce the actual language becomes evident. According to the form of tests for GCSE, there are two or three of fifty questions relating to language functions. Not many, but to give the correct answer in the important examination is the desire of all of the students. As an English teacher, I do the research for focusing on the functions of language so as to properly equip students to complete assigned tasks. Therefore; I choose the theme “Guide the students in class 12 A1, 12A2 at Quan Son high school to distinguish the language functions and responses exercises effectively” as my research. I hope that the information in this paper will be helpful in getting a deeper look about language functions and responses in English. AIMS OF THE STUDY. Each work has its own aims, so does this study. The aims of my study are: To help students master English more and develop skills of group-work. To fulfill my career passion and improve my teaching skills. Help improve and enrich the student’s vocabulary and basic grammar structures. Help the students understand the various options that regulate their choices of language functions and responses. Help myself to have a good document to review for my students more effectively so that they are able to cope with the exercises related to language functions and response s in their exams more easily. Exchange the other teachers slight experiences in teaching the language functions and responses at school. THE RESEARCHED SUBJECTS. 1. Scope : Researching in the process of teaching English in class 12 A1, 12A2 including 75 students at Quan Son high school. 2. Object: This subject is concerned with the lessons about functional language in the text book English 10,11,12. IV. METHOD OF THE STUDY. Studying the documents dealing with the theme ( mainly the information on the Google) Using analytic methods Observing and asking colleagues for ideas and experiences Practicing the application of the study Because of the limit scale of the initiative I will give only common patterns and exercises which are usually used in the official English tests in Viet Nam. Especially, there are both written test and multiple choices in English test for GCSE and examination for the gifted students. So, I am sure that my students will be able to feel more confident when they take the test after they understand deeply the language functions and responses as well as related forms of the exercises. PART B: CONTENT THEORICAL FOUNDATION OF THIS RESEARCH. There are many different languages in our world that are different. And each language has its rule. Language function is a part of the language. Also, each language has its function, which is used to communicate. Moreover, language function makes us communicate correctly. If we don't know about language function, the sentences that we talk to other people will not complete. Although the listeners can understand, but it can change the its meaning. As we are teachers, we should be careful in teaching the function of language because if we teach a wrong function, it means that the students will receive a wrong language system, too. Therefore, the teachers should be careful about the usage of verbs or tenses, phrases, structures and vocabulary because these are the main factors that we can make our students write or speak English correctly. Nowadays, there are many ways to teach the students to learn language functions. Some students think that language functions are boring. Then, they don't want to learn. Many students feel afraid and confused when they have to face to some exercises like filling in the gaps in these sentences, choosing the suitable responses, in particularly, in the tests for gifted students and GCSE. Many learners make a lot of mistakes and they are often penalized for these mistakes in examinations. Throughout the lessons I lecture for my students in order to help the students solve their problems I decided to study this theme based on primary causes: Reading the reference books and websites related language functions and responses. Discussing with other teachers. Applying in teaching. Observing and drawing out experience. THE CURRENT SITUATION OF THE ISSUE. As a teacher of English, I have often noticed my students having problem in learning functions of language. Theoretically, they learn even much better than we expect but practically they find struggling with basic functions of language. I was shocked the first time when I heard students having difficulties in choosing and using appropriate language functions. Here students were found to be lack of knowledge of language functions. To improve the existing problem since then I started to think of and look for the proper ways and techniques of teaching language functions in order to make them capable to use in appropriate. Therefore, I, as a teacher, read different articles and books regarding how to teach language functions to make it easier for my students to use language functions and came up with some ideas. In order that the students can overcome the difficulties in this contemporary situation and they can know, understand also apply knowledge which they are contributed in doing the exercises better and better. Through studying myself, exchanging with my colleagues as well as observing and investigating the learning method of students in real lessons I would like to give solutions to the problems. I truly hope that this subject will be a meaningful document for readers THE SOLUTIONS TO SOLVE THE MATTER. Language functions refer to the purposes in which we use language to communicate. We use language for a variety of formal and informal purposes, and specific grammatical structures and vocabulary are often used with each language function. If we think about a function of language as one that serves a purpose we can see that much of what we see can be considered to be functional. Each of these individual utterances is considered functions of language. Some examples of language functions include:[1] Compare and contrast Persuasion Asking questions Expressing likes and dislikes Cause and effect Summarizing Sequencing Predicting Agreeing/disagreeing Greeting people/introductions[1] When teaching about language functions, it is important that teachers explicitly teach the vocabulary and phrases associated with each language function. It is important that as students become familiar with the vocabulary associated with each language function that more advanced functional vocabulary is introduced to the students. In addition to functional vocabulary, students must also be introduced to grammatical structures associated with each language function. English learners must be provided with ample opportunities to practice the vocabulary and grammatical structures associated with language functions in both oral and written contexts. Functional vocabulary and grammatical structures can be differentiated for students at varying proficiency levels, with students at the lower levels of English proficiency practicing easier vocabulary and grammatical structures than students at higher levels of English proficiency. Firstly, I give the students the general tips so that they can recognize functional language in the sentences. Ghi chú:.Mục III từ “language functions Introductions” tác giả tham khảo từ TLTK [1] General tips Identifying the types of the questions. If the language function is a question about the information, we need to understand what kind of this question is Yes/No or Wh- question because each kind of the question has one equivalent response. For instance, a question with has an answer with an adverbial of time such as five days ago, last year, in 2015, etc Yes/ No questions have the responses beginning with Yes or No. The exercise is quite easy for the students to cope with it. Example: [2] 1. Linda: Excuse me. Where’s the post office? Maria: -------------------- It’s over there. B. I’m afraid not. C. Don’t worry. D. Yes, I think so. Answer key: A (Adapted from: đề thi TNTHPT,hệ 7 năm, năm 2008) “A” is the correct option. The students may make mistake with option “B” because of its beginning with “Yes”. However it is incorrect grammar (yes, it has). “C” and “D” are wrong. Identifying special functional language. Generally, there are a lot of questions which the students have to choose the options referring to not only what functions they can use with those situations, but also the language culture rather than asking to know information. These questions are difficult for the students if they are not taught about language functions clearly. The function of the language is something to control the meaning or expression of the communication. To cope with these difficult questions the students need to do the steps following: Recognize the communicative function of the sentence Think about the responses the students have studied. Read the options given, and then choose the most suitable options. Speaking language is different from written one and culture from English countries is also different from its Vietnam. Therefore, If the students are not taught specific grammatical structures and vocabularies for a variety of formal and informal purposes they will find it confusing to give correct answer. Functional vocabulary and grammatical structures can be differentiated for students in order that the students can do the task quickly and exactly. Ghi chú :Mục 1.1 phần Example tác giả tham khảo từ TLTK [2]. Example : (Adapted from : Đề thi ĐH-CĐ năm 2008)[2] Jane: “Do you feel like going to the cinema this evening? Susan: “----------“ Which choice is correct in this situation. Option A and B seem to be true, however, when refusing an invitation the English don’t often say in a direct way like that. So, Option C is the best choice. Note: to test the language function in examinations there are some questions asking indicating the sentence that is closest in meaning. It is essential that the students should identify the language function in the saying then find out the suitable reported speech. Example: Mark the letter A, B, C or D to indicate the sentence that is closest in meaning to the following question. “Stop smoking or you’ll be ill” The doctor told me. The doctor advised me to give up smoking to avoid illness. I was ordered not to smoke to recover from illness. I was warned against smoking a lot of cigarettes. The doctor suggested smoking to treat illness. Obviously, The meaning of the saying is an advisory, so the choice must be “A” Using logical thinking. It is truly that, sometimes the students don’t know how to give the answer. In this case, the students should understand and base on the meaning of the sentence and logic and speculation to give the answer. Example: [2] Maria: “ I’m taking my end of term examination tomorrow” Sarah: “_________” Good luck B. Good day C. Good time D. Good chance Answer key: A( adapted from : Đề thi TNTHPT lần 2,năm 2008) Using grammatical knowledge. In addition to functional vocabulary, students must also be introduced to grammatical structures associated with each language function. For example, when teaching the language function of compare/contrast,teachers might teach comparative adjectives (i.e., smaller than, more expensive than, etc) or Ghi chú: Trong trang này phần ví dụ tác giả tham khảo từ TLTK [2] superlative adjectives (i.e., smallest, most expensive).Some choices may be wrong because of incorrect grammar. Example: [3] “Don’t you like folk music?” “___________” Yes, I don’t B. No, I like it a lot C. Yes, I love it D. It’s nice If the language function is expressed in special structures, the students had better study the grammatical structures of them. Example: [3] “Could I go out with Tom, Mom?” “_____________” Yes, of course B. Yes, you could C. Yes, you can D.A and C The answer key is “D”. “Could I go out with Tom, Mom?” indicates the permission. We can’t use “Could” in the response for asking permission with “Could”. Using the synonym and the antonym. It is vital for the learners that they focus on the words or phrases which have closest and opposite meaning even compare/ contrast structures. When teaching about language functions, it is important that teachers explicitly teach the vocabulary and phrases associated with each language function. Example: [3] “Mary dances beautifully” “_________________” Yeah, She’s a wonderful dancer. B. True. She dances badly. C. Right. She’s a clumsy dancer. D. Yeah, so terribly. “A” is an exact choice due to the same meaning with the root sentence. “B”, “C”, “D” has the contrast meaning of it. Generally, I only point out the students to know the kinds of the exercises in general tips. To assist the students to identify the different language functions and responses in a specific way I show them in the part following. Language Functions and Responses. A lot of what we say is for a specific purpose. Whether we are apologizing, expressing a wish or asking permission, we use language in order to fulfill that purpose. Each purpose can be known as a language function. One function can have many different language functions. Here are the examples of different functions: Ghi chú: Mục phần ví dụ tác giả tham khảo từ TLTK [3] If you say anything, I will tell your parents. (Function-Threat/Warning) I'll do the hovering, if you do the washing up. (Function-Negotiation) I'll go to the shops for you. (Function-Offer) And one function can be expressed using several different language structures. For example: If I were you, I'd ..... (2nd conditional) Why don't you ...... (Present tense - question - negative) You should / ought .... (Modal/auxiliary verb) Therefore, In the second part I show for the students different purposes in thesaying called language function by dividing the amount of knowledge into each function. And each kind I list the phrases, structures the students will meet. When the students understand it clearly they will be certainly confident to do the related exercises. 2.1 Asking for information. Kinds of question Content Examples[3] 1 Yes/No question This kind of question often begins with auxiliaries such as Are, Is, Am, Was, Were, Does, Did, Can, Could, Have, Had, Will, Would, The response often (not always) begins with “yes/ no” and repeats the auxiliary. A: Do you like classical music? B: Yes. I do ( not Yes, I like)/ No, I don’t ( not No, I don’t like) Sometimes, the answer only begins with “yes”, “no” and may be it can repeat the auxiliary or not, in addition it gives more information to its answer. A: Did you get the tickets? B: Yes, Two days ago Sometimes The answer doesn’t absolutely begin with yes, no. A: Is there enough gas in the car? B: I just filled it yesterday. Be careful with the negative question. For this question, if you agree you say “No”, in contrary if you disagree you say “Yes” A: Haven’t you repaired the car yet? B: yes, I did it yesterday The yes/ no questions are shown in tag questions. A: He usually gets up late, doesn’t he? B: Yes, He does. 2 I think so./ I’m afraid not. The response can begin with some phrases such as I think so, I believe so, instead of using yes or no. Using “so” after think, be afraid, believe, expect, guess, hope, suppose. Not using “so” after know or be sure. In the answer having negative meaning we can use “So” for some verbs such as think, believe, expect and suppose and NOT use for some verbs such as hope, guess, suppose, believe and be afraid.( suppose and believe may be used both not and so). A: Is Peter coming to the party? B: I think so A : Do you think he will get the job? B: I don’t think so 3 Choice questions. The choice questions often use “or” as a conjunction and The response asks giving one of two given choices. Yes or No isn’t used in the situation. A: Are they coming tonight or tomorrow? B: Tonight/ They are coming tonight. 4 Who(m) / whose questions “Who” works as a subject and refers to a person or an organizer. In negative question Who(m) refers to an object related to a person Whose +N A: Who came to see you? B: Jane and Eric A: who didn’t do the home work ? B: I didn’t A: Whose book did you borrow? B: Mary’s 5 What questions “What questions’ diverse so the students have to pay attention to vocabulary, grammar, tenses and pronouns of the question. “What” is a subject as well as an object. Note: What +be+ like?(How) What + look+ . Like?( asking about the appearance) A: What does your father look like? B: He’s very tall. 6 How questions Asking about a process or the way to do something. The answer contains the preposition “by” or an adverb. Asking about the quantity and status quo. The response includes some adjectives such as: not too bad, fine, excellent, How + Adj / Adv A: How do you go to school every day? B: By bike A: How was the film? B: Fantastic A: How far is it from your house to the school? B: About three kilometers. 7 Why questions Asking about the reason. The answer often begins with because/because of/ due to. Be careful with Why don’t we/you? A: Why did he fail the exam? B: Because he didn’t prepare well enough for it. 8 Where questions Asking about the place. A: Where did you go last night? B: I went to my friend’s house. 9 When questions Asking about the time A; when will the war be over? B: very soon Asking for permission. Asking for permission Agreeing Disagreeing Okay if I ? Is it OK if I ..? Can/ Could I .? Is it alright if I..? Could I possibly ? Do you mind? May I. Sure Sure, go ahead Of course. Yes, you can. Yes, here you are Not at all No, of course not No, go ahead No, Please do Yes , you may Well, I’d rather you didn’t Sorry. I’m afraid that I’m sorry, but No, You can’t Example: [2] . -Tom: “Can I bring a friend to your birthday party?-Kyle: “..” A. It’s my honor. B. Let’s do it then C. The more the merrier D. That’s right ( Adapted from : Kỳ t
Tài liệu đính kèm:
 guide_the_students_in_class_12_a1_12a2_at_quan_son_high_scho.docx
guide_the_students_in_class_12_a1_12a2_at_quan_son_high_scho.docx



